TRANSITORY FLORA: Organisms that have been acquired recently by the contact with another person or object. They are acquired through the contact with the patients or infected personnel or colonized or with the polluted surfaces. The organisms vary and they depend on their origin. And coli, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus negative gram, Klebsiella and pneumoniae are temporarily in the workers' of the health hands. These organisms survive in the skin for several periods (from some minutes until several hours or days)
FLORA RESIDENT: organisms that live and they multiply in the skin and they vary of a person to other, they are in general, of low virulence and in strange occasions they cause infections located in the skin. Most of the organisms residents are in the superficial layers of the skin, approximately of 10% to 20% live in the deep epidermal layers and in general they are not pathogens. Among the organisms considered as flora resident the Staphilococus of negative coagulase they are included.
ANTI-MICROBIAL SOAP: Soap that an agent anti-microbial associate contains.
SOCIAL HAND WASH: Is defined as a rub brief of all the surfaces of the hands with soap, followed by mouthwash to the jet of water. Their objective is to remove the dirt,
CLINICAL LAUNDRY: Is defined as a rub brief and energetic of all the surfaces of the hands with anti-microbial solution, followed by rinse of to the jet of water. It looks for to remove the dirt, the organic material and to diminish the concentration of the transitory flora, acquired by recent contact with patient or fómites.
SANITIZACION: The sanitation is defined as a rub brief with antiseptic solution starting from alcohol and emollient, looking for to destroy the microorganisms of the transitory, acquired bacterial flora recently for direct contact with patients, relatives or fómites and to diminish the flora resident. Provided the hands are clean and without contamination with organic material.
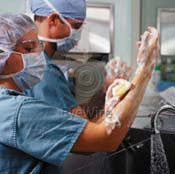
SURGICAL HANDWASH: Is defined as a rub energetic of all the surfaces of the hands until the elbows with antimicrobial solution, followed by mouthwash to the jet of water. It looks for to eliminate, the transitory flora and to diminish the concentration of bactteries of the flora resident.
(E. Larson, Ek KretzaR. Compliance with hand washing and barrier precautions. J. Hospital Infection 1995)